IoT (Internet of Things), can be defined as a link for software, telecom, and electronic hardware industry and promises to offer tremendous opportunities for a range of industries. When applied to manufacturing industry it is popularly known as IIoT or Industry 4.0 and is often not a stand-alone term.
It is actually, an amalgamation of different technologies like machine learning, big data, sensor data, M2M communication, robotics, analytics, and automation that have existed in the industrial backdrop for several years now.
Industrial Revolutions as they happened:
It is a name given to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies incorporating cyber physical systems.
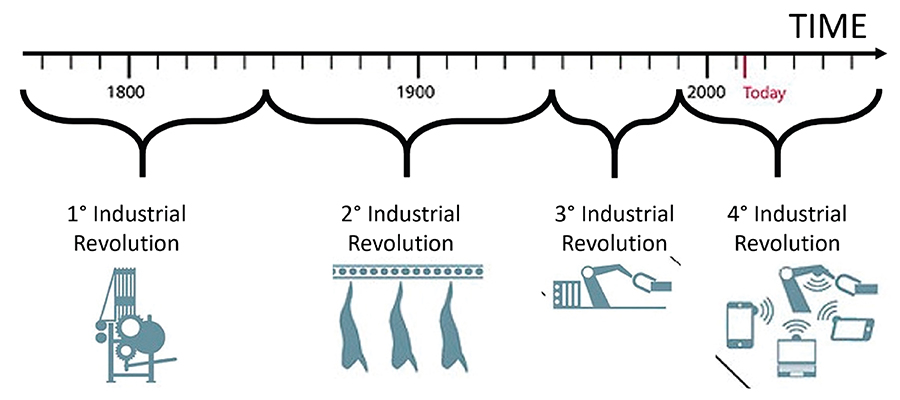
Image Courtesy: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/7/1/36/htm
Industry 1.0 (1784)
The invention of steam engines kick started the Industry 1.0. However, the manufacturing was purely labour oriented and tiresome.
Industry 2.0 (1870)
The first assembly line production was introduced. This invention was a big relief for the workers as their labour was minimized to the possible extent. Henry Ford the Father of mass production and the assembly line introduced the process.
Industry 3.0 (1969)
Involved advancement of electronic technology and industrial robotics. Miniaturization of the circuit boards through programmable logic controllers, Industrial robotics to simplify, automate and increase the production. However, the operations still remained isolated from the entire enterprise.
Industry 4.0 (2010)
The vision of connected enterprise through interconnecting industrial assets through the internet was fulfilled with the introduction of Industry 4.0. These smart devices communicate with each other through packets of signals and generate tons of data which upon analysis bring out insights, valuable in more than one ways. IoT offers with it the advantages of asset optimization, production integration, smart monitoring, remote diagnosis, intelligent decision making and most importantly the feature of Predictive
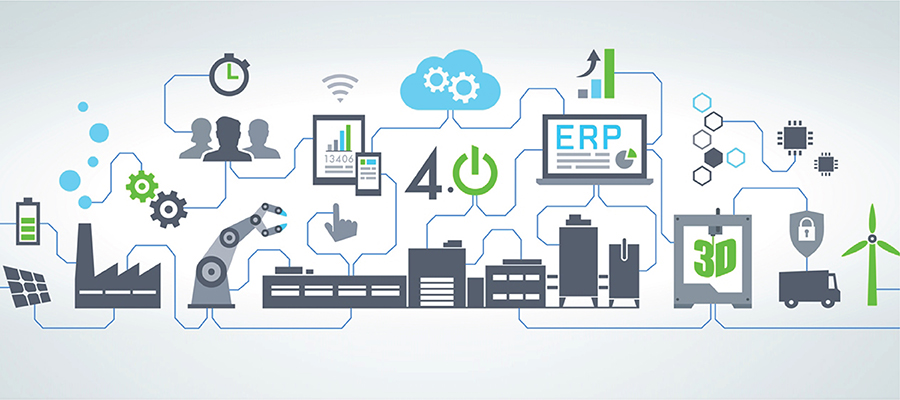
Image Courtesy: https://blog.gigamon.com/2017/05/31/industry-4-0-autonomous-customizable-flexible-manufacturing/smart-factory/
Impacts of IoT
As per the popular forecasts
- 30 billion devices will be available for IoT by 2020 (Excluding smartphones).
- $18 trillion value of added economic activity from the consumer and industrial IoT in next 20 years.
This clearly states that there will be massive amount of data exchange between the devices and will help predicting a great deal of performance, outputs, situations and much more to take precautionary/corrective actions.
Based on these facts, it is all set that with the introduction of data connectivity of machines across the shop floor, there will be massive amount of betterment in the outputs. Alongside, enlisted are some of the other positive impacts that are apparent:
- Predictive & Proactive maintenance
- Real-Time Monitoring
- Asset/Resource Optimization
- Remote Diagnosis
- Enhanced efficiency
Industry Used Cases: The changing face of manufacturing industry
For instance, Alibaba, the online retail giant has opened the largest smart warehouse in China manned by 60 cutting-edge robots. These Wi-Fi-equipped, self-charging machines are responsible for moving goods across the warehouse with guided and tracked manoeuvring. These intelligent robots send the goods to human workers, who then arrange the products to be packed and posted to customers around the world.
Another example is that of Siemens Electronics, Germany, who uses IoT in machines and computers for handling 75% of the production efforts autonomously. Once the product’s parts are produced, they are able to communicate with the machines through product codes which navigate the machines further in the production process.
Cisco is yet another significant example that uses IoT in its manufacturing exceptionally well. Since they have outsourced production plants worldwide, they have developed “VMES” or “virtual” manufacturing execution system platforms to keep a close eye on the production. The system uses technology like the cloud, IoT and many more to gather the data from production machines in real time and thereby predict quality capabilities in the outsourced surrounding using Data Analytics options.
Risks associated: IoT Hackers paradise
There is a school of thoughts who consider this transformation as hackers’ paradise. As for the argument, several named companies like BMW, General Motors and Mercedes-Benz have all been the victim of hackers’ attack through remotely operating links on smartphone apps. Fiat Chrysler had to issue a recall because its infotainment system allowed hackers to seize control of its vehicles.
Final opinions
These cases brings us to a juncture that is suggestive of a though narrating the idea of great controls yet the dire need of improvements for betterment. It says that although there have been significant developments in field of manufacturing with the fourth industrial revolution the issue of data security still needs massive attention to ensure successful implementation and reduced risk factors.